
Inteligentne aplikacje internetowe Laboratorium 3 Użycie klasyfikatorów z pakietu WEKI w kodzie Javy |
Kod każdego ćwiczenia zapisz w oddzielnym pliku w projekcie (Eclipse lub NetBeans)
Ćwiczenie 1. Budowa klasyfikatora (WEKI in Java)
Wczytaj dane
Utwórz klasyfikatora (J48)
Wyświetl na konsoli dostępne właściwości klasyfikatora

Ćwiczenie 2.
Wczytaj dane
Utwórz klasyfikator (k-nn) (weka.classifiers.lazy.IBk)
Wyświetl na konsoli dostępne właściwości klasyfikatora
Ćwiczenie 3. Ewaluacja klasyfikatora (CV)
Dokonaj ewaluacji zbudowanych klasyfikatorów
Wypisz statystyki z ewaluacji, wyświetl macierz pomyłek

PS. Cross-validation If you only have a training set and no test you might want to evaluate the classifier by using 10 times 10-fold cross-validation. This can be very easily done via the Evaluation class. Here we seed the random selection of our folds for the CV with 1. Check out the Evaluation class for more information about the statistics it produces. Note: The classifier (in our example tree) is not supposed to be trained when handed over to the crossValidateModel method. Why? If the classifier does not abide to the Weka conventions, that a classifier has to be re-initialized every time the buildClassifier method is called (in other words: subsequent calls to the buildClassifier method always return the same results), you will get inconsistent and worthless results. The crossValidateModel takes care of training and evaluating the classifier (it creates a copy of the original classifier that you hand over to the crossValidateModel for each run of the cross-validation). Some methods for retrieving the results from the evaluation:
|
Ćwiczenie 4.Ustawianie opcji klasyfikatora
Utwórz klasyfikator J48 z opcją bez przycinania drzewa
Utwórz klasyfikator k-NN z opcją 3 najbliższych sąsiadów
Porównaj wyniki ewaluacji
import weka.classifiers.trees.J48; ... String[] options = new String[1]; options[0] = "-U"; // unpruned tree J48 tree = new J48(); // new instance of tree tree.setOptions(options); // set the options tree.buildClassifier(data); // build classifier |
NAME weka.classifiers.lazy.IBk SYNOPSIS K-nearest neighbours classifier. Can select appropriate value of K based on cross-validation. Can also do distance weighting. For more information, see D. Aha, D. Kibler (1991). Instance-based learning algorithms. Machine Learning. 6:37-66. OPTIONS KNN -- The number of neighbours to use. |
NAME weka.classifiers.trees.J48 SYNOPSIS Class for generating a pruned or unpruned C4.5 decision tree. For more information, see Ross Quinlan (1993). C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Mateo, CA. |
Ćwiczenie 5. Klasyfikowanie nowych przykładów podanych w pliku arff
Utwórz plik arff z przykładami bez podanej klasy decyzyjnej (unlabeled.arff)
Dokonaj klasyfikacji obydwoma klasyfikatorami przykładów wczytanych z pliku (unlabeled.arff)
Zapisz wyniki klasyfikacji w pliku labeled.arff
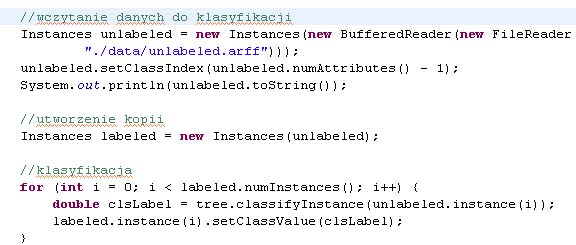
PS. In case you have an unlabeled dataset that you want to classify with your newly trained classifier, you can use the following code snippet. It loads the file /some/where/unlabeled.arff, uses the previously built classifier tree to label the instances, and saves the labeled data as /some/where/labeled.arff. Note on nominal classes:
|
Wydział Informatyki, Politechnika Białostocka |